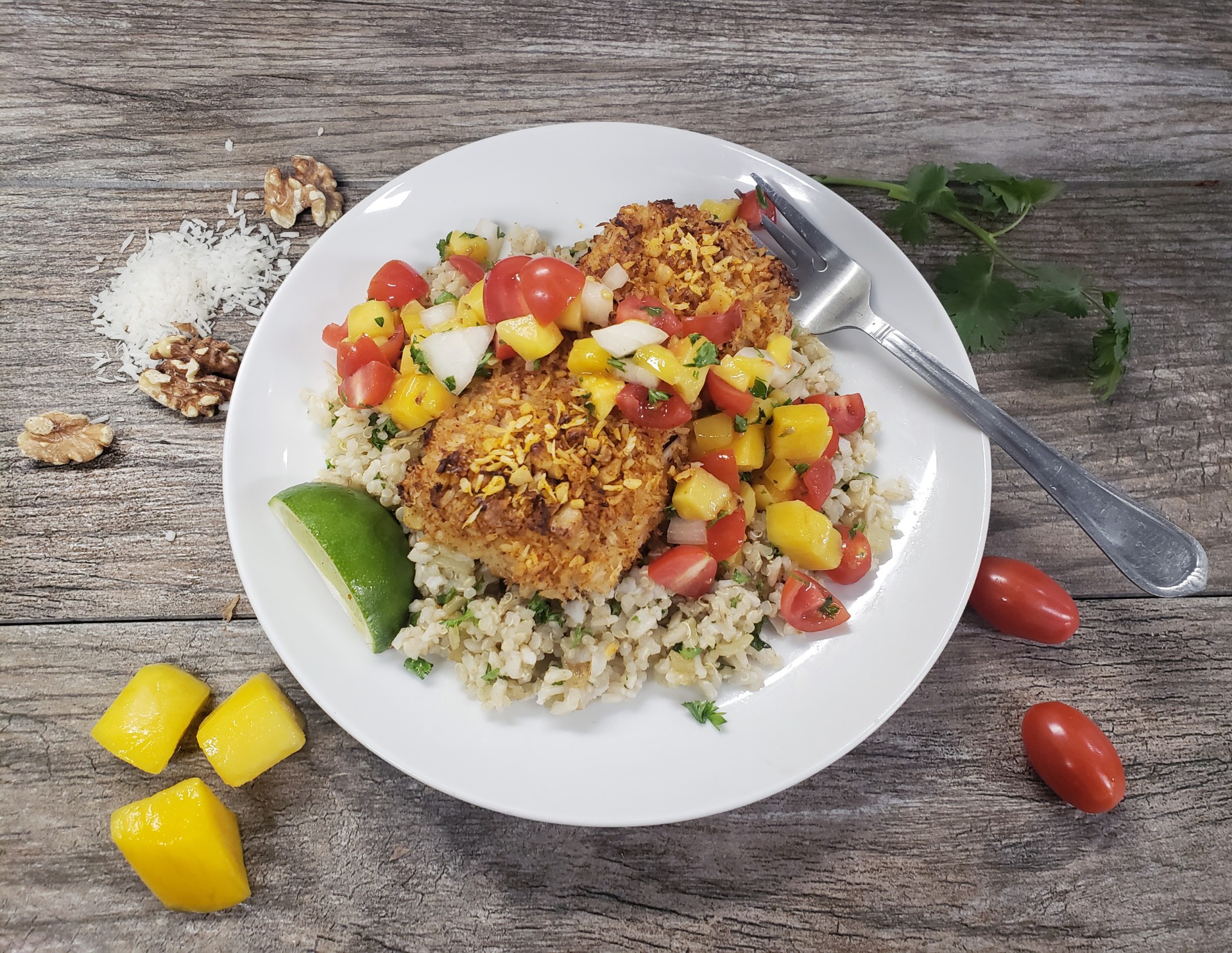
Joint inflammation can cause discomfort and affect daily life. While medical treatments play a crucial role, adopting an anti-inflammatory diet can provide additional support in managing joint inflammation. Certain foods have been associated with anti-inflammatory properties and may help alleviate symptoms. In this blog, we will explore diets that can reduce joint inflammation.
- Mediterranean Diet: The Mediterranean diet is renowned for its health benefits, including its potential to reduce inflammation. This eating pattern emphasizes whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and healthy fats like olive oil. It also includes moderate consumption of fish, lean proteins, and limited intake of red meat. Research published in the journal Nutrients suggests that the Mediterranean diet’s anti-inflammatory effects can help alleviate joint inflammation and related symptoms.
- Anti-Inflammatory Fatty Acids: Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids into your diet can help combat inflammation. Fatty fish, such as salmon, are excellent sources of omega-3s and vegetarian sources include flaxseed, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and walnuts. These fatty acids have been shown to inhibit the production of inflammatory substances in the body.
- Colorful Fruits and Vegetables: Colorful fruits and vegetables are packed with antioxidants and phytochemicals that possess anti-inflammatory properties. Incorporate a variety of deeply colored produce, such as berries, cherries, leafy greens, bell peppers, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts, into your meals. These vibrant foods contain essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that help combat inflammation and promote overall health.
- Herbs and Spices: Certain herbs and spices have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties. Turmeric, ginger, cinnamon, and garlic, for example, have been studied for their potential to reduce inflammation. Curcumin, a compound found in turmeric, has demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects in numerous studies.
- Whole Grains and Legumes: Whole grains and legumes offer a host of nutrients, fiber, and phytochemicals that may help reduce inflammation. Opt for whole grain options like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread, and include legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans in your diet.
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet can provide valuable support in managing joint inflammation. We incorporate all of these diet ideas into the our dishes at Cuisine for healing, and we make all of our recipes accessible through our cookbook!
Sources:
- Dinu, M., et al. (2018). Mediterranean Diet and Multiple Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies and Randomized Trials. Nutrients, 10(8), 1036.
- Calder, P. C. (2017). Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes. Nutrients, 9(11), 1170.